If a greenhouse gas absorbs directly in the region of the IR spectrum in which Earth emits large amounts of IR radiation, this gas will have a significant warming effect. By absorbing in this region, the greenhouse gas will prevent a greater amount of IR radiation from escaping into space than it would if it absorbed in a region in which the Earth did not emit as much IR radiation. Additionally, molecules that absorb IR at a shorter wavelength have more of an effect than those that absorb at longer wavelengths. Since shorter wavelengths are more energetic, molecules that absorb them prevent more energy from being emitted into space.
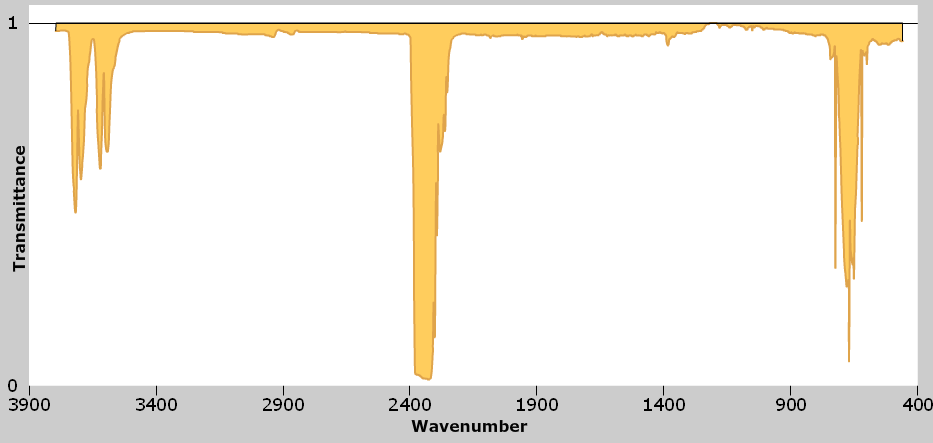
How strongly a greenhouse gas absorbs IR radiation is also important. The strength of absorption is indicated in the IR spectrum by the intensity of the absorption peaks; peaks that extend to the bottom of the graph (zero transmittance) indicate stronger absorption of IR radiation. Use the IR Windows Learning Tool to observe the IR spectrum of carbon dioxide. Does carbon dioxide strongly absorb IR radiation?
Question For Thought
Having observed the region of the IR spectrum in which carbon dioxide absorbs, as well as how strongly carbon dioxide absorbs, do you think these factors suggest that carbon dioxide is a significant or an insignificant greenhouse gas? Refer to the IR Windows Learning Tool as necessary.